Compare commits
9 Commits
4342a1f3e5
...
master
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
0f23a4b477 | ||
|
|
49f64f509b | ||
|
|
e264921831 | ||
|
|
4cd76a8d81 | ||
|
|
69564f5750 | ||
|
|
6c938f751d | ||
|
|
7fcb9f1056 | ||
|
|
69d975bac9 | ||
|
|
d3336bab00 |
6
.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
6
.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
|
|||||||
|
*.o
|
||||||
|
enumerate
|
||||||
|
graph
|
||||||
|
output/
|
||||||
|
old/
|
||||||
|
README.html
|
||||||
11
Makefile
11
Makefile
@@ -4,17 +4,10 @@ HEADERS=weyl.h thickenings.h queue.h bitvec.h
|
|||||||
#SPECIAL_OPTIONS=-O3 -pg -funroll-loops -fno-inline
|
#SPECIAL_OPTIONS=-O3 -pg -funroll-loops -fno-inline
|
||||||
SPECIAL_OPTIONS=-O3 -flto -funroll-loops -Winline
|
SPECIAL_OPTIONS=-O3 -flto -funroll-loops -Winline
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
OPTIONS=-m64 -march=native -mtune=native -std=gnu99 -D_GNU_SOURCE $(SPECIAL_OPTIONS)
|
OPTIONS=-m64 -march=native -std=gnu99 -D_GNU_SOURCE $(SPECIAL_OPTIONS)
|
||||||
NAME=enumerate-balanced-ideals
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
all: enumerate graph
|
all: enumerate graph
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$(NAME).tar.bz2: $(NAME) $(HEADERS) enumerate.c weyl.c thickenings.c
|
|
||||||
tar cjhf $(NAME).tar.bz2 $(NAME)/enumerate.c $(NAME)/weyl.c $(NAME)/thickenings.c $(NAME)/weyl.h $(NAME)/thickenings.h $(NAME)/queue.h $(NAME)/bitvec.h $(NAME)/Makefile $(NAME)/graph.c
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$(NAME):
|
|
||||||
ln -s . $(NAME)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
enumerate: enumerate.o weyl.o thickenings.o
|
enumerate: enumerate.o weyl.o thickenings.o
|
||||||
gcc $(OPTIONS) -o enumerate enumerate.o thickenings.o weyl.o
|
gcc $(OPTIONS) -o enumerate enumerate.o thickenings.o weyl.o
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -34,4 +27,4 @@ graph.o: graph.c $(HEADERS)
|
|||||||
gcc $(OPTIONS) -c graph.c
|
gcc $(OPTIONS) -c graph.c
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
clean:
|
clean:
|
||||||
rm -f enumerate graph thickenings.o weyl.o enumerate.o graph.o $(NAME) $(NAME).tar.bz2
|
rm -f enumerate graph thickenings.o weyl.o enumerate.o graph.o
|
||||||
|
|||||||
74
README.md
Normal file
74
README.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
|
|||||||
|
# Enumerate balanced ideals #
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
A program to enumerate balanced ideals in [Weyl groups]. These are subsets of the Weyl group W which are ideals with respect to the Bruhat order and which are mapped to their complement by the involution on W which is given by left-multiplication with the longest element.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Balanced ideals were used by [Kapovich-Leeb-Porti] to construct cocompact domains of discontinuity in flag manifolds for the action of Anosov representations. Essentially, their result says that, if P and Q are two parabolic subgroups of a Lie group G and W its restricted Weyl group, then for every P-Anosov representation and every balanced ideal in W which is left-invariant by P∩W and right-invariant by Q∩W, there is one cocompact domain of discontinuity in the flag manifold G/Q.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
As the number of balanced ideals grows superexponentially with the rank of the Lie group, we have made some effort to optimize the enumeration algorithm. For example, the ideals are stored as bit vectors, so that set operations can be realized as bitwise operations. Also, only half of the ideal is stored, as the other half can be reconstructed from the balanced condition. With these and some other tricks we get an algorithm which can find tens of millions of balanced ideals per second on a single core (although outputting them is a lot slower, so this is mostly useful for determining the number of balanced ideals).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Setup ##
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
You need a terminal, gcc, and GNU Make. Navigate to the folder and run `make`. This produces the executables `enumerate` and `graph`. Their usage is described below.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Usage ##
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
In the most basic case, we just specify a Weyl / Coxeter group by giving its [Cartan type] as the first argument, for example C3, G2, A1A2 (for the direct product of A1 and A2) etc. The output will be a list of all balanced ideals. For example:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ ./enumerate A3
|
||||||
|
A3
|
||||||
|
Rank: 3 Order: 24 Positive Roots: 6 Cosets: 24
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Balanced ideals:
|
||||||
|
0 left: a c right: ab gen: caba
|
||||||
|
1 left: a c right: bc gen: abcb
|
||||||
|
2 left: right: gen: cba acb abc
|
||||||
|
3 left: right: gen: cba acb aba bc
|
||||||
|
4 left: right: gen: cba abc bac
|
||||||
|
5 left: right: a gen: cba aba bac
|
||||||
|
6 left: right: gen: acb abc bcb ba
|
||||||
|
7 left: right: b gen: acb aba bcb
|
||||||
|
8 left: right: c gen: abc bac bcb
|
||||||
|
9 left: b right: gen: aba bac bcb
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Found 10 balanced ideals
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
There is one line for each balanced ideal. The first column is an index, the next two columns show the left- and right-invariance of the ideal as a subset of the generators `a,b,c` of the Weyl group (see below for an explanation of the labeling). Finally a minimal generating set of the balanced ideal is shown, in the sense that it is the smallest ideal containing these Weyl group elements.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
If we are only interested in balanced ideal with a certain left- and right-invariance, we cangive these as the second and third arguments. The subsets will be divided out in the beginning and the enumeration algorithm will run on the double cosets, making this also a lot faster.. The empty set can be specified as "-", so `enumerate A4 - -` does the same as `enumerate A4`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ ./enumerate C5 a bcde
|
||||||
|
<a> \ C5 / <bcde>
|
||||||
|
Rank: 5 Order: 3840 Positive Roots: 25 Cosets: 16
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Balanced ideals:
|
||||||
|
0 left: abcd right: bcde gen: bcdabcaba
|
||||||
|
1 left: ab de right: bcde gen: edbcaba
|
||||||
|
2 left: a cd right: bcde gen: cdbcaba edcba
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Found 3 balanced ideals
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Finally, we can control the amount of output using the environment variable OUTPUT_LEVEL. Values from 0 to 4 are valid. The default is 2. For example:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- `OUTPUT_LEVEL=0` means no output at all. This is rarely useful.
|
||||||
|
- `OUTPUT_LEVEL=1` only shows the number of balanced ideals (in addition to some basic info about the group). This is currently the only mode that can take full advantage of the speed of the enumeration algorithm.
|
||||||
|
- `OUTPUT_LEVEL=2` (the default) additionally prints one line for every balanced ideal found, as explained above.
|
||||||
|
- `OUTPUT_LEVEL=3` additionally shows the list of all double cosets, giving a minimal wordlength representative for each of them.
|
||||||
|
- `OUTPUT_LEVEL=4` prints the same, and also the Bruhat order on the double cosets as a dot file (which can be rendered by Graphviz), and the involution on the double quotient. If you only want to see the Bruhat order, it is better to use the `graph` tool, which is made specifically for that.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
$ OUTPUT_LEVEL=1 ./enumerate C4
|
||||||
|
C4
|
||||||
|
Rank: 4 Order: 384 Positive Roots: 16 Cosets: 384
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Found 49404510 balanced ideals
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Labeling of the Weyl group generators ##
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
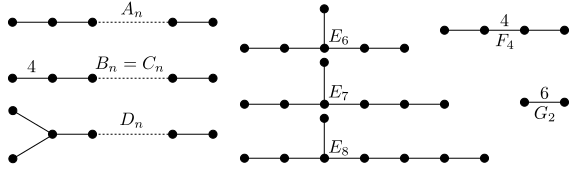
The allowed Cartan types are `An`, `Bn`, `Cn`, `Dn`, `E6`, `E7`, `E8`, `F4` and `G2`, where n is any positive integer, plus any direct products of them. The Coxeter group generators / simple roots are labeled `a,b,c,d,...`, first by direct factor, and then from left to right in the following diagram. So for example in the Cartan type `C2C3`, the generators are `a,b,c,d,e`, with the products `ab` and `cd` having order 4, `de` having order 3 and any other pair commuting.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[Kapovich-Leeb-Porti]: https://arxiv.org/abs/1306.3837
|
||||||
|
[Weyl groups]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Weyl_group
|
||||||
|
[Cartan type]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Semisimple_Lie_algebra#Classification
|
||||||
81
graph.c
81
graph.c
@@ -1,16 +1,15 @@
|
|||||||
#include "weyl.h"
|
|
||||||
#include "queue.h"
|
#include "queue.h"
|
||||||
|
#include "weyl.h"
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#include <strings.h>
|
|
||||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
|
||||||
#include <memory.h>
|
#include <memory.h>
|
||||||
|
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||||
|
#include <strings.h>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
static char* alphabetize(weylgroup_element_t *e, char *str)
|
static char *alphabetize(weylgroup_element_t *e, char *str) {
|
||||||
{
|
if (e->wordlength == 0)
|
||||||
if(e->wordlength == 0)
|
|
||||||
sprintf(str, "1");
|
sprintf(str, "1");
|
||||||
else {
|
else {
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < e->wordlength; j++)
|
for (int j = 0; j < e->wordlength; j++)
|
||||||
str[j] = e->word[j] + 'a';
|
str[j] = e->word[j] + 'a';
|
||||||
str[e->wordlength] = 0;
|
str[e->wordlength] = 0;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
@@ -18,8 +17,7 @@ static char* alphabetize(weylgroup_element_t *e, char *str)
|
|||||||
return str;
|
return str;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
|
int main(int argc, const char *argv[]) {
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
semisimple_type_t type;
|
semisimple_type_t type;
|
||||||
unsigned long right_invariance, left_invariance;
|
unsigned long right_invariance, left_invariance;
|
||||||
doublequotient_t *dq;
|
doublequotient_t *dq;
|
||||||
@@ -30,43 +28,72 @@ int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
|
|||||||
ERROR(argc < 2, "Too few arguments!\n");
|
ERROR(argc < 2, "Too few arguments!\n");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
type.n = 0;
|
type.n = 0;
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < argc - 1; i++) {
|
for (int i = 0; i < argc - 1; i++) {
|
||||||
if(argv[i+1][0] < 'A' || argv[i+1][0] > 'G')
|
if (argv[i + 1][0] < 'A' || argv[i + 1][0] > 'G')
|
||||||
break;
|
break;
|
||||||
type.n++;
|
type.n++;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
type.factors = (simple_type_t*)malloc(type.n*sizeof(simple_type_t));
|
type.factors = (simple_type_t *)malloc(type.n * sizeof(simple_type_t));
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < type.n; i++) {
|
for (int i = 0; i < type.n; i++) {
|
||||||
type.factors[i].series = argv[i+1][0];
|
type.factors[i].series = argv[i + 1][0];
|
||||||
type.factors[i].rank = argv[i+1][1] - '0';
|
type.factors[i].rank = argv[i + 1][1] - '0';
|
||||||
ERROR(argv[i+1][0] < 'A' || argv[i+1][0] > 'G' || argv[i+1][1] < '1' || argv[i+1][1] > '9', "Arguments must be Xn with X out of A-G and n out of 1-9\n");
|
ERROR(argv[i + 1][0] < 'A' || argv[i + 1][0] > 'G' ||
|
||||||
|
argv[i + 1][1] < '1' || argv[i + 1][1] > '9',
|
||||||
|
"Arguments must be Xn with X out of A-G and n out of 1-9\n");
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
left_invariance = right_invariance = 0;
|
left_invariance = right_invariance = 0;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if(argc - type.n >= 3) {
|
if (argc - type.n >= 3) {
|
||||||
if(strcmp(argv[type.n + 1], "-") != 0)
|
if (strcmp(argv[type.n + 1], "-") != 0)
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < strlen(argv[type.n + 1]); i++)
|
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(argv[type.n + 1]); i++)
|
||||||
left_invariance |= (1 << (argv[type.n + 1][i] - 'a'));
|
left_invariance |= (1 << (argv[type.n + 1][i] - 'a'));
|
||||||
if(strcmp(argv[type.n + 2], "-") != 0)
|
if (strcmp(argv[type.n + 2], "-") != 0)
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < strlen(argv[type.n + 2]); i++)
|
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(argv[type.n + 2]); i++)
|
||||||
right_invariance |= (1 << (argv[type.n + 2][i] - 'a'));
|
right_invariance |= (1 << (argv[type.n + 2][i] - 'a'));
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// generate graph
|
// generate graph
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
dq = weyl_generate_bruhat(type, left_invariance, right_invariance);
|
dq = weyl_generate_bruhat(type, left_invariance, right_invariance);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
fprintf(stdout, "digraph test123 {\n");
|
// color ideals
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < dq->count; i++)
|
int *color = (int*) malloc(dq->count * sizeof(int));
|
||||||
for(doublecoset_list_t *current = dq->cosets[i].bruhat_lower; current; current = current->next)
|
memset(color, 0, dq->count * sizeof(int));
|
||||||
fprintf(stdout, "%s -> %s;\n",
|
for(int i = type.n+3; i < argc; i++) {
|
||||||
|
weylgroup_element_t *elem = &dq->group[0]; // identity
|
||||||
|
for(int j = 0; j < strlen(argv[i]); j++) {
|
||||||
|
int gen = argv[i][j] - 'a';
|
||||||
|
elem = elem->right[gen];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
color[elem->coset->index] = 1;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for(int i = dq->count - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
|
||||||
|
if(color[i] > 0) {
|
||||||
|
for(doublecoset_list_t *current = dq->cosets[i].bruhat_lower; current; current = current->next) {
|
||||||
|
color[current->to->index] = color[i];
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
fprintf(stdout, "digraph bruhat {\n");
|
||||||
|
for (int i = 0; i < dq->count; i++) {
|
||||||
|
fprintf(stdout, "%s [color=\"%s\"];\n",
|
||||||
alphabetize(dq->cosets[i].min, stringbuffer),
|
alphabetize(dq->cosets[i].min, stringbuffer),
|
||||||
alphabetize(current->to->min, stringbuffer2));
|
color[i] > 0 ? "red" : "black");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for (doublecoset_list_t *current = dq->cosets[i].bruhat_lower; current; current = current->next) {
|
||||||
|
fprintf(stdout, "%s -> %s [color=\"%s\"];\n",
|
||||||
|
alphabetize(dq->cosets[i].min, stringbuffer),
|
||||||
|
alphabetize(current->to->min, stringbuffer2),
|
||||||
|
color[i] > 0 ? "red" : "black");
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
fprintf(stdout, "}\n\n");
|
fprintf(stdout, "}\n\n");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// clean up
|
// clean up
|
||||||
weyl_destroy_bruhat(dq);
|
weyl_destroy_bruhat(dq);
|
||||||
|
free(color);
|
||||||
free(type.factors);
|
free(type.factors);
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -1,74 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
#include "weyl.h"
|
|
||||||
#include "queue.h"
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#include <limits.h>
|
|
||||||
#include <string.h>
|
|
||||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
static char* alphabetize(weylgroup_element_t *e, char *str)
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
if(e->wordlength == 0)
|
|
||||||
sprintf(str, "1");
|
|
||||||
else {
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < e->wordlength; j++)
|
|
||||||
str[j] = e->word[j] + 'a';
|
|
||||||
str[e->wordlength] = 0;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return str;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
semisimple_type_t type;
|
|
||||||
simple_type_t simple;
|
|
||||||
char buf[100];
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
simple.series = 'A';
|
|
||||||
simple.rank = atoi(argv[1]);
|
|
||||||
type.n = 1;
|
|
||||||
type.factors = &simple;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
int order = weyl_order(type);
|
|
||||||
doublequotient_t *dq = weyl_generate_bruhat(type, 0, 0);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
queue_t q;
|
|
||||||
int cur;
|
|
||||||
int *viewed = (int*)malloc(order*sizeof(int));
|
|
||||||
int found;
|
|
||||||
int minimum = INT_MAX;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < order; i++) {
|
|
||||||
found = 0;
|
|
||||||
memset(viewed, 0, order*sizeof(int));
|
|
||||||
queue_init(&q);
|
|
||||||
queue_put(&q, dq->cosets[i].opposite->index);
|
|
||||||
while((cur = queue_get(&q)) != -1) {
|
|
||||||
if(cur == i) { // found what we were looking for
|
|
||||||
// printf("foo: %d %d\n", i, dq->cosets[i].min->wordlength);
|
|
||||||
found = 1;
|
|
||||||
break;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
for(doublecoset_list_t *current = dq->cosets[cur].bruhat_lower; current; current = current->next) {
|
|
||||||
if(!viewed[current->to->index]) {
|
|
||||||
viewed[current->to->index] = 1;
|
|
||||||
queue_put(&q, current->to->index);
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
if(!found) {
|
|
||||||
printf("%s %d not found\n", alphabetize(dq->cosets[i].min, buf), dq->cosets[i].min->wordlength);
|
|
||||||
if(dq->cosets[i].min->wordlength < minimum)
|
|
||||||
minimum = dq->cosets[i].min->wordlength;
|
|
||||||
// break;
|
|
||||||
} else {
|
|
||||||
printf("%s %d found\n", alphabetize(dq->cosets[i].min, buf), dq->cosets[i].min->wordlength);
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
printf("Minimum l(w) such that w0w can be in a balanced ideal: %d\n", minimum);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
free(viewed);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return 0;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
312
old/coxeter.c
312
old/coxeter.c
@@ -1,312 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
#include "coxeter.h"
|
|
||||||
#include "queue.h"
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#include <memory.h>
|
|
||||||
#include <gsl/gsl_linalg.h>
|
|
||||||
#include <gsl/gsl_blas.h>
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
static void applyGenerator(int i, double *x, double *y, int rank, double **schlaefliMatrix)
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
memcpy(y, x, rank*sizeof(double));
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < rank; j++)
|
|
||||||
y[i] -= schlaefliMatrix[i][j]*x[j];
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
static int check_equal_sector(gsl_matrix *x1, gsl_matrix *x2, gsl_matrix *yinv, gsl_matrix *schlaefli, gsl_vector *starting, gsl_vector *i1, gsl_vector *i2)
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
double scalarProduct;
|
|
||||||
int rank = x1->size1;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// calculate <y^{-1} * x1 * x2 * s, e_i> for all i, or identically the components of schlaefli*y^{-1}*x*s
|
|
||||||
gsl_blas_dgemv(CblasNoTrans, 1.0, x2, starting, 0.0, i1);
|
|
||||||
gsl_blas_dgemv(CblasNoTrans, 1.0, x1, i1, 0.0, i2);
|
|
||||||
gsl_blas_dgemv(CblasNoTrans, 1.0, yinv, i2, 0.0, i1);
|
|
||||||
gsl_blas_dgemv(CblasNoTrans, 1.0, schlaefli, i1, 0.0, i2);
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < rank; i++)
|
|
||||||
if(gsl_vector_get(i2, i) < 0)
|
|
||||||
return 0;
|
|
||||||
return 1;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
static void invert(gsl_matrix *x, gsl_matrix *xinv)
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
int rank = x->size1;
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix *xLU = gsl_matrix_alloc(rank, rank);
|
|
||||||
gsl_permutation *p = gsl_permutation_alloc(rank);
|
|
||||||
int s;
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_memcpy(xLU, x);
|
|
||||||
gsl_linalg_LU_decomp(xLU, p, &s);
|
|
||||||
gsl_linalg_LU_invert(xLU, p, xinv);
|
|
||||||
gsl_permutation_free(p);
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_free(xLU);
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
static void generate_schlaefli_matrix(semisimple_type_t type, gsl_matrix *mat)
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_set_zero(mat);
|
|
||||||
int offset = 0;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for(int k = 0; k < type.n; k++) {
|
|
||||||
if(type.factors[k].series == 'A') {
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < type.factors[k].rank; i++)
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < type.factors[k].rank; j++)
|
|
||||||
if(i == j)
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_set(mat, offset + i, offset + j, 2.0);
|
|
||||||
else if(i - j == 1 || i - j == -1)
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_set(mat, offset + i, offset + j, -1.0);
|
|
||||||
} else if(type.factors[k].series == 'B' || type.factors[k].series == 'C') {
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < type.factors[k].rank; i++)
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < type.factors[k].rank; j++)
|
|
||||||
if(i == j)
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_set(mat, offset + i, offset + j, 2.0);
|
|
||||||
else if(i == 0 && j == 1 || i == 1 && j == 0)
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_set(mat, offset + i, offset + j, -sqrt(2.0));
|
|
||||||
else if(i - j == 1 || i - j == -1)
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_set(mat, offset + i, offset + j, -1.0);
|
|
||||||
} else if(type.factors[k].series == 'D') {
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < type.factors[k].rank; i++)
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < type.factors[k].rank; j++)
|
|
||||||
if(i == j)
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_set(mat, offset + i, offset + j, 2.0);
|
|
||||||
else if(i > 0 && j > 0 && (i - j == 1 || i - j == -1) || i == 0 && j == 2 || i == 2 && j == 0)
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_set(mat, offset + i, offset + j, -1.0);
|
|
||||||
} else if(type.factors[k].series == 'F') {
|
|
||||||
ERROR(type.factors[k].rank != 4, "A Coxeter group of type %c%d does not exist or is not implemented!\n", type.factors[k].series, type.factors[k].rank);
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_set(mat, offset + i, offset + i, 2.0);
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_set(mat, offset + i, offset + i + 1, i == 1 ? -sqrt(2.0) : -1.0);
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_set(mat, offset + i + 1, offset + i, i == 1 ? -sqrt(2.0) : -1.0);
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
} else if(type.factors[k].series == 'G') {
|
|
||||||
ERROR(type.factors[k].rank != 2, "A Coxeter group of type %c%d does not exist or is not implemented!\n", type.factors[k].series, type.factors[k].rank);
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_set(mat, offset + 0, offset + 0, 2.0);
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_set(mat, offset + 0, offset + 1, -sqrt(3.0));
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_set(mat, offset + 1, offset + 0, -sqrt(3.0));
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_set(mat, offset + 1, offset + 1, 2.0);
|
|
||||||
} else {
|
|
||||||
ERROR(1, "A Coxeter group of type %c%d does not exist or is not implemented!\n", type.factors[k].series, type.factors[k].rank);
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
offset += type.factors[k].rank;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
int coxeter_rank(semisimple_type_t type)
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
int rank = 0;
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < type.n; i++)
|
|
||||||
rank += type.factors[i].rank;
|
|
||||||
return rank;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
int coxeter_order(semisimple_type_t type)
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
int order = 1;
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < type.n; i++) {
|
|
||||||
if(type.factors[i].series == 'A') { // (rank+1)!
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 1; j <= type.factors[i].rank + 1; j++)
|
|
||||||
order *= j;
|
|
||||||
} else if(type.factors[i].series == 'B' || type.factors[i].series == 'C') { // 2^rank * rank!
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 1; j <= type.factors[i].rank; j++)
|
|
||||||
order *= 2*j;
|
|
||||||
} else if(type.factors[i].series == 'D') { // 2^(rank-1) * rank!
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 2; j <= type.factors[i].rank; j++)
|
|
||||||
order *= 2*j;
|
|
||||||
} else if(type.factors[i].series == 'E') {
|
|
||||||
if(type.factors[i].rank == 6)
|
|
||||||
order *= 51840;
|
|
||||||
else if(type.factors[i].rank == 7)
|
|
||||||
order *= 2903040;
|
|
||||||
else if(type.factors[i].rank == 8)
|
|
||||||
order *= 696729600;
|
|
||||||
else
|
|
||||||
ERROR(1, "A Coxeter group of type %c%d does not exist or is not implemented!\n", type.factors[i].series, type.factors[i].rank);
|
|
||||||
} else if(type.factors[i].series == 'F') {
|
|
||||||
ERROR(type.factors[i].rank != 4, "A Coxeter group of type %c%d does not exist or is not implemented!\n", type.factors[i].series, type.factors[i].rank);
|
|
||||||
order *= 1152;
|
|
||||||
} else if(type.factors[i].series == 'G') {
|
|
||||||
ERROR(type.factors[i].rank != 2, "A Coxeter group of type %c%d does not exist or is not implemented!\n", type.factors[i].series, type.factors[i].rank);
|
|
||||||
order *= 12;
|
|
||||||
} else if(type.factors[i].series == 'H') {
|
|
||||||
if(type.factors[i].rank == 2)
|
|
||||||
order *= 10;
|
|
||||||
else if(type.factors[i].rank == 3)
|
|
||||||
order *= 120;
|
|
||||||
else if(type.factors[i].rank == 4)
|
|
||||||
order *= 14400;
|
|
||||||
else
|
|
||||||
ERROR(1, "A Coxeter group of type %c%d does not exist or is not implemented!\n", type.factors[i].series, type.factors[i].rank);
|
|
||||||
} else {
|
|
||||||
ERROR(1, "A Coxeter group of type %c%d does not exist or is not implemented!\n", type.factors[i].series, type.factors[i].rank);
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
return order;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
int coxeter_hyperplanes(semisimple_type_t type)
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
int hyperplanes = 0;
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < type.n; i++) {
|
|
||||||
if(type.factors[i].series == 'A') // rank*(rank+1)/2
|
|
||||||
hyperplanes += (type.factors[i].rank * (type.factors[i].rank + 1)) / 2;
|
|
||||||
else if(type.factors[i].series == 'B' || type.factors[i].series == 'C') // rank * rank
|
|
||||||
hyperplanes += type.factors[i].rank * type.factors[i].rank;
|
|
||||||
else if(type.factors[i].series == 'D') // rank * (rank - 1)
|
|
||||||
hyperplanes += type.factors[i].rank * (type.factors[i].rank - 1);
|
|
||||||
else if(type.factors[i].series == 'E') {
|
|
||||||
if(type.factors[i].rank == 6)
|
|
||||||
hyperplanes += 36;
|
|
||||||
else if(type.factors[i].rank == 7)
|
|
||||||
hyperplanes += 63;
|
|
||||||
else if(type.factors[i].rank == 8)
|
|
||||||
hyperplanes += 120;
|
|
||||||
else
|
|
||||||
ERROR(1, "A Coxeter group of type %c%d does not exist or is not implemented!\n", type.factors[i].series, type.factors[i].rank);
|
|
||||||
} else if(type.factors[i].series == 'F') {
|
|
||||||
ERROR(type.factors[i].rank != 4, "A Coxeter group of type %c%d does not exist or is not implemented!\n", type.factors[i].series, type.factors[i].rank);
|
|
||||||
hyperplanes += 24;
|
|
||||||
} else if(type.factors[i].series == 'G') {
|
|
||||||
ERROR(type.factors[i].rank != 2, "A Coxeter group of type %c%d does not exist or is not implemented!\n", type.factors[i].series, type.factors[i].rank);
|
|
||||||
hyperplanes += 6;
|
|
||||||
} else {
|
|
||||||
ERROR(1, "A Coxeter group of type %c%d does not exist or is not implemented!\n", type.factors[i].series, type.factors[i].rank);
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
return hyperplanes;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
unsigned long opposition_involution(semisimple_type_t type, unsigned long theta)
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
int offset = 0;
|
|
||||||
unsigned long result = 0;
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < type.n; i++) {
|
|
||||||
unsigned long current = (theta >> offset) & ((1 << type.factors[i].rank) - 1);
|
|
||||||
unsigned long iota_current;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if(type.factors[i].series == 'B' || type.factors[i].series == 'C' || type.factors[i].series == 'F' || type.factors[i].series == 'G') {
|
|
||||||
iota_current = current;
|
|
||||||
} else if(type.factors[i].series == 'A') {
|
|
||||||
iota_current = 0;
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < type.factors[i].rank; j++)
|
|
||||||
iota_current += ((current >> j) & 1) << (type.factors[i].rank - 1 - j);
|
|
||||||
} else if(type.factors[i].series == 'D') {
|
|
||||||
if(type.factors[i].rank % 2 == 0) {
|
|
||||||
iota_current = current;
|
|
||||||
} else {
|
|
||||||
ERROR(1, "The opposition involution for type %c%d is not yet implemented!\n", type.factors[i].series, type.factors[i].rank);
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
} else if(type.factors[i].series == 'E') {
|
|
||||||
ERROR(1, "The opposition involution for En is not yet implemented!\n");
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
result += iota_current << offset;
|
|
||||||
offset += type.factors[i].rank;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return result;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
static void generate_starting_vector(int rank, gsl_matrix *schlaefli, gsl_vector *result)
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix *schlaefliLU = gsl_matrix_alloc(rank, rank);
|
|
||||||
gsl_vector *diagonal = gsl_vector_alloc(rank);
|
|
||||||
gsl_permutation *p = gsl_permutation_alloc(rank);
|
|
||||||
int s;
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < rank; i++)
|
|
||||||
gsl_vector_set(diagonal, i, 1.0);
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_memcpy(schlaefliLU, schlaefli);
|
|
||||||
gsl_linalg_LU_decomp(schlaefliLU, p, &s);
|
|
||||||
gsl_linalg_LU_solve(schlaefliLU, p, diagonal, result);
|
|
||||||
gsl_permutation_free(p);
|
|
||||||
gsl_vector_free(diagonal);
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_free(schlaefliLU);
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
void generate_coxeter_graph(semisimple_type_t type, int *result)
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
int rank = coxeter_rank(type);
|
|
||||||
int order = coxeter_order(type);
|
|
||||||
int element_count;
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix *schlaefliMatrix = gsl_matrix_alloc(rank, rank);
|
|
||||||
gsl_vector *startingVector = gsl_vector_alloc(rank);
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix *generators = (gsl_matrix*)malloc(rank*sizeof(gsl_matrix));
|
|
||||||
double *generators_data = (double*)malloc(rank*rank*rank*sizeof(double));
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix *elements = (gsl_matrix*)malloc(order*sizeof(gsl_matrix));
|
|
||||||
double *elements_data = (double*)malloc(rank*rank*order*sizeof(double));
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix *inverses = (gsl_matrix*)malloc(order*sizeof(gsl_matrix));
|
|
||||||
double *inverses_data = (double*)malloc(rank*rank*order*sizeof(double));
|
|
||||||
gsl_vector *i1 = gsl_vector_alloc(rank);
|
|
||||||
gsl_vector *i2 = gsl_vector_alloc(rank);
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix *current_element = gsl_matrix_alloc(rank, rank);
|
|
||||||
queue_t queue;
|
|
||||||
int current;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < rank; i++)
|
|
||||||
generators[i] = gsl_matrix_view_array(generators_data + i*rank*rank, rank, rank).matrix;
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < order; i++)
|
|
||||||
elements[i] = gsl_matrix_view_array(elements_data + i*rank*rank, rank, rank).matrix;
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < order; i++)
|
|
||||||
inverses[i] = gsl_matrix_view_array(inverses_data + i*rank*rank, rank, rank).matrix;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
generate_schlaefli_matrix(type, schlaefliMatrix);
|
|
||||||
generate_starting_vector(rank, schlaefliMatrix, startingVector);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < rank; i++) {
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_set_identity(&generators[i]);
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < rank; j++)
|
|
||||||
if(i == j)
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_set(&generators[i], i, j, -1.0);
|
|
||||||
else
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_set(&generators[i], i, j, -gsl_matrix_get(schlaefliMatrix, i, j));
|
|
||||||
// gsl_matrix_fprintf(stdout, &generators[i], "%f");
|
|
||||||
// printf("\n");
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
queue_init(&queue);
|
|
||||||
queue_put(&queue, 0);
|
|
||||||
element_count = 1;
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_set_identity(&elements[0]);
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_set_identity(&inverses[0]);
|
|
||||||
while((current = queue_get(&queue)) != -1) {
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < rank; i++) {
|
|
||||||
int j;
|
|
||||||
for(j = 0; j < element_count; j++) {
|
|
||||||
if(check_equal_sector(&generators[i], &elements[current], &inverses[j], schlaefliMatrix, startingVector, i1, i2)) { // generators[i] * elements[current] = elements[j]
|
|
||||||
result[rank*current + i] = j;
|
|
||||||
break;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
// if no existing element equals generators[i] * elements[current], create one
|
|
||||||
if(j == element_count) {
|
|
||||||
ERROR(element_count >= order, "Got more elements than the order of the group should be!\n");
|
|
||||||
gsl_blas_dgemm(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, 1.0, &generators[i], &elements[current], 0.0, &elements[element_count]);
|
|
||||||
invert(&elements[element_count], &inverses[element_count]);
|
|
||||||
result[rank*current + i] = element_count;
|
|
||||||
queue_put(&queue, element_count);
|
|
||||||
element_count++;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
ERROR(element_count != order, "Something went wrong building the Coxeter group. Found %d elements, %d expected\n", element_count, order);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
/*
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < order; i++) {
|
|
||||||
printf("%d: ", i);
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < rank; j++)
|
|
||||||
printf("%d ", result[rank*i + j]);
|
|
||||||
printf("\n");
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
*/
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
gsl_vector_free(startingVector);
|
|
||||||
gsl_vector_free(i1);
|
|
||||||
gsl_vector_free(i2);
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_free(schlaefliMatrix);
|
|
||||||
gsl_matrix_free(current_element);
|
|
||||||
free(generators);
|
|
||||||
free(elements);
|
|
||||||
free(generators_data);
|
|
||||||
free(elements_data);
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
#ifndef COXETER_H
|
|
||||||
#define COXETER_H
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
typedef struct {
|
|
||||||
char series;
|
|
||||||
int rank;
|
|
||||||
} simple_type_t;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
typedef struct {
|
|
||||||
int n;
|
|
||||||
simple_type_t *factors;
|
|
||||||
} semisimple_type_t;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
void generate_coxeter_graph(semisimple_type_t type, int *result);
|
|
||||||
int coxeter_order(semisimple_type_t type);
|
|
||||||
int coxeter_hyperplanes(semisimple_type_t type);
|
|
||||||
int coxeter_rank(semisimple_type_t type);
|
|
||||||
unsigned long opposition_involution(semisimple_type_t type, unsigned long theta);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#endif
|
|
||||||
@@ -1,193 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
|
||||||
#include <string.h>
|
|
||||||
#include <sys/stat.h>
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#include "thickenings.h"
|
|
||||||
#include "coxeter.h"
|
|
||||||
#include "queue.h"
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#define SWAP(t, a, b) do {t tmp = a; a = b; b = tmp;} while(0)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
char *stringify_SLn1_permutation(int *word, int wordlength, int rank, char *str)
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i <= rank; i++)
|
|
||||||
str[i] = '1' + i;
|
|
||||||
str[rank+1] = 0;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < wordlength; i++) {
|
|
||||||
char tmp = str[word[i]];
|
|
||||||
str[word[i]] = str[word[i]+1];
|
|
||||||
str[word[i]+1] = tmp;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
return str;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
char *stringify_Onn1_permutation(int *word, int wordlength, int rank, char *str)
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i <= rank*2; i++)
|
|
||||||
str[i] = '1' + i;
|
|
||||||
str[2*rank+1] = 0;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < wordlength; i++) {
|
|
||||||
if(word[i] == 0)
|
|
||||||
SWAP(char, str[rank-1], str[rank+1]);
|
|
||||||
else {
|
|
||||||
SWAP(char, str[rank-word[i]], str[rank-word[i]-1]);
|
|
||||||
SWAP(char, str[rank+word[i]], str[rank+word[i]+1]);
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
return str;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
FILE *infile;
|
|
||||||
struct stat st;
|
|
||||||
int rank, order, hyperplanes;
|
|
||||||
semisimple_type_t type;
|
|
||||||
int n;
|
|
||||||
signed char *level;
|
|
||||||
node_t *graph;
|
|
||||||
int *left, *right;
|
|
||||||
int left_invariant, right_invariant;
|
|
||||||
int left_invariant_wanted = 0, right_invariant_wanted = 0;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
unsigned long left_invariance, right_invariance;
|
|
||||||
edgelist_t *edgelists;
|
|
||||||
int *words;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
queue_t queue;
|
|
||||||
int current;
|
|
||||||
int *seen;
|
|
||||||
int *generators;
|
|
||||||
int ngens;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
char string_buffer1[1000];
|
|
||||||
const char *alphabet = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// parse arguments
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if(argc < 2)
|
|
||||||
infile = stdin;
|
|
||||||
else {
|
|
||||||
if(strcmp(argv[1], "-") == 0)
|
|
||||||
infile = stdin;
|
|
||||||
else
|
|
||||||
infile = fopen(argv[1], "rb");
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if(argc >= 4) {
|
|
||||||
if(strcmp(argv[2], "-") != 0)
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < strlen(argv[2]); i++)
|
|
||||||
left_invariant_wanted |= (1 << (argv[2][i] - 'a'));
|
|
||||||
if(strcmp(argv[3], "-") != 0)
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < strlen(argv[3]); i++)
|
|
||||||
right_invariant_wanted |= (1 << (argv[3][i] - 'a'));
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
fread(&type.n, sizeof(int), 1, infile); // we completely trust the input data
|
|
||||||
type.factors = malloc(type.n * sizeof(simple_type_t));
|
|
||||||
fread(type.factors, sizeof(simple_type_t), type.n, infile);
|
|
||||||
fread(&left_invariance, sizeof(simple_type_t), type.n, infile);
|
|
||||||
fread(&right_invariance, sizeof(simple_type_t), type.n, infile);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// get graph
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
rank = coxeter_rank(type);
|
|
||||||
order = coxeter_order(type);
|
|
||||||
hyperplanes = coxeter_hyperplanes(type);
|
|
||||||
ERROR(strlen(alphabet) < rank, "The alphabet has too few letters\n");
|
|
||||||
seen = (int*)malloc(order*sizeof(int));
|
|
||||||
generators = (int*)malloc(order*sizeof(int));
|
|
||||||
level = (signed char*)malloc(order*sizeof(int));
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
graph = graph_alloc(type);
|
|
||||||
prepare_graph(type, graph);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// finally do stuff
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
int counter = 0;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
while(fread(level, sizeof(signed char), order, infile) == order) {
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
/*
|
|
||||||
if((counter++) % 100000 == 0)
|
|
||||||
print_thickening(rank, order, level, 0, 0, 0, alphabet, stdout);
|
|
||||||
continue;
|
|
||||||
*/
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
left_invariant = right_invariant = -1; // all 1s
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < order; j++) {
|
|
||||||
for(int k = 0; k < rank; k++) {
|
|
||||||
if(level[j] > 0 && level[graph[j].left[k]] < 0 || level[j] < 0 && level[graph[j].left[k]] > 0) {
|
|
||||||
left_invariant &= ~(1 << k);
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
if(level[j] > 0 && level[graph[j].right[k]] < 0 || level[j] < 0 && level[graph[j].right[k]] > 0) {
|
|
||||||
right_invariant &= ~(1 << k);
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if((~left_invariant & left_invariant_wanted) == 0 && (~right_invariant & right_invariant_wanted) == 0) {
|
|
||||||
ngens = 0;
|
|
||||||
memset(generators, 0, order*sizeof(int));
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < order; j++) {
|
|
||||||
if(level[j] == HEAD_MARKER && generators[j] == 0) { // ignore the generator, if it is equivalent to one already seen
|
|
||||||
ngens++;
|
|
||||||
queue_init(&queue);
|
|
||||||
queue_put(&queue, j);
|
|
||||||
while((current = queue_get(&queue)) != -1) {
|
|
||||||
if(generators[current] == 0) { // visit everyone only once
|
|
||||||
generators[current] = ngens;
|
|
||||||
for(int k = 0; k < rank; k++) {
|
|
||||||
if(left_invariant & (1 << k))
|
|
||||||
queue_put(&queue, graph[current].left[k]);
|
|
||||||
if(right_invariant & (1 << k))
|
|
||||||
queue_put(&queue, graph[current].right[k]);
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
printf("left: ");
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < rank; j++)
|
|
||||||
printf("%c", left_invariant & (1 << j) ? alphabet[j] : ' ');
|
|
||||||
printf(" right: ");
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < rank; j++)
|
|
||||||
printf("%c", right_invariant & (1 << j) ? alphabet[j] : ' ');
|
|
||||||
printf(" generators: ");
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
memset(seen, 0, order*sizeof(int));
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < order; i++) {
|
|
||||||
if(generators[i] != 0 && seen[generators[i]-1] == 0) {
|
|
||||||
seen[generators[i]-1] = 1;
|
|
||||||
// if(type.n == 1 && type.factors[0].series == 'A')
|
|
||||||
// printf("%s ", stringify_SLn1_permutation(graph[i].word, graph[i].wordlength, rank, string_buffer1));
|
|
||||||
// else if(type.n == 1 && (type.factors[0].series == 'B' || type.factors[0].series == 'C'))
|
|
||||||
// printf("%s ", stringify_Onn1_permutation(graph[i].word, graph[i].wordlength, rank, string_buffer1));
|
|
||||||
// else
|
|
||||||
if(i == 0)
|
|
||||||
printf("1 ");
|
|
||||||
else
|
|
||||||
printf("%s ", alphabetize(graph[i].word, graph[i].wordlength, alphabet, string_buffer1));
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
printf("\n");
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if(infile != stdin)
|
|
||||||
fclose(infile);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// cleanup
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
graph_free(type, graph);
|
|
||||||
free(seen);
|
|
||||||
free(generators);
|
|
||||||
free(type.factors);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return 0;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
189
old/process.c
189
old/process.c
@@ -1,189 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
|
||||||
#include <string.h>
|
|
||||||
#include <sys/stat.h>
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#include "thickenings.h"
|
|
||||||
#include "weyl.h"
|
|
||||||
#include "queue.h"
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
FILE *infile;
|
|
||||||
semisimple_type_t type;
|
|
||||||
unsigned long left_invariance, right_invariance; // these are the invariances we have already modded out
|
|
||||||
unsigned long left_invariant, right_invariant; // these are the invariances of the thickening under consideration
|
|
||||||
int rank, cosets;
|
|
||||||
node_t *graph;
|
|
||||||
signed char *thickening;
|
|
||||||
int *seen, *generators;
|
|
||||||
queue_t queue;
|
|
||||||
int ngenerators;
|
|
||||||
int current;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
char string_buffer1[1000];
|
|
||||||
const char *alphabet = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if(argc < 2)
|
|
||||||
infile = stdin;
|
|
||||||
else
|
|
||||||
infile = fopen(argv[1], "rb");
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// we completely trust the input data
|
|
||||||
ERROR(fread(&type.n, sizeof(int), 1, infile) == 0, "The input file seems to be empty!\n");
|
|
||||||
type.factors = malloc(type.n * sizeof(simple_type_t));
|
|
||||||
fread(type.factors, sizeof(simple_type_t), type.n, infile);
|
|
||||||
fread(&left_invariance, sizeof(simple_type_t), type.n, infile);
|
|
||||||
fread(&right_invariance, sizeof(simple_type_t), type.n, infile);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
rank = weyl_rank(type);
|
|
||||||
graph = graph_alloc(type);
|
|
||||||
cosets = prepare_simplified_graph(type, left_invariance, right_invariance, graph);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
thickening = (signed char*)malloc(cosets*sizeof(signed char));
|
|
||||||
generators = (int*)malloc(cosets*sizeof(int));
|
|
||||||
seen = (int*)malloc(cosets*sizeof(int));
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
while(fread(thickening, sizeof(signed char), cosets, infile) == cosets) {
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// determine invariances of this thickening
|
|
||||||
left_invariant = right_invariant = -1; // set all bits to 1
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < cosets; j++) {
|
|
||||||
for(int k = 0; k < rank; k++) {
|
|
||||||
if(thickening[j] > 0 && thickening[graph[j].left[k]] < 0 ||
|
|
||||||
thickening[j] < 0 && thickening[graph[j].left[k]] > 0)
|
|
||||||
left_invariant &= ~(1 << k);
|
|
||||||
if(thickening[j] > 0 && thickening[graph[j].right[k]] < 0 ||
|
|
||||||
thickening[j] < 0 && thickening[graph[j].right[k]] > 0)
|
|
||||||
right_invariant &= ~(1 << k);
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// print this stuff
|
|
||||||
printf("left: ");
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < rank; j++)
|
|
||||||
printf("%c", left_invariant & (1 << j) ? alphabet[j] : ' ');
|
|
||||||
printf(" right: ");
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < rank; j++)
|
|
||||||
printf("%c", right_invariant & (1 << j) ? alphabet[j] : ' ');
|
|
||||||
printf(" generators: ");
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// find a minimal set of weyl group elements such that the union of the ideals generated by their cosets wrt the invariances determined above gives the thickening
|
|
||||||
// in the first step, mark everything which is equivalent to a "head" by a generator id
|
|
||||||
ngenerators = 0;
|
|
||||||
memset(generators, 0, cosets*sizeof(int));
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < cosets; j++) {
|
|
||||||
if(thickening[j] == HEAD_MARKER && generators[j] == 0) { // ignore the generator, if it is equivalent to one already seen
|
|
||||||
ngenerators++;
|
|
||||||
queue_init(&queue);
|
|
||||||
queue_put(&queue, j);
|
|
||||||
while((current = queue_get(&queue)) != -1) {
|
|
||||||
if(generators[current] == 0) { // visit everyone only once
|
|
||||||
generators[current] = ngenerators;
|
|
||||||
for(int k = 0; k < rank; k++) {
|
|
||||||
if(left_invariant & (1 << k))
|
|
||||||
queue_put(&queue, graph[current].left[k]);
|
|
||||||
if(right_invariant & (1 << k))
|
|
||||||
queue_put(&queue, graph[current].right[k]);
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// in the second step, go through the list in ascending word length order and print the first appearance of each generator id
|
|
||||||
memset(seen, 0, cosets*sizeof(int));
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < cosets; i++) {
|
|
||||||
if(generators[i] != 0 && seen[generators[i]-1] == 0) {
|
|
||||||
seen[generators[i]-1] = 1;
|
|
||||||
printf("%s ", alphabetize(graph[i].word, graph[i].wordlength, alphabet, string_buffer1));
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
printf("\n");
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if(infile != stdin)
|
|
||||||
fclose(infile);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
graph_free(type, graph);
|
|
||||||
free(type.factors);
|
|
||||||
free(thickening);
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
/*******************************************************************************************
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
seen = (int*)malloc(order*sizeof(int));
|
|
||||||
generators = (int*)malloc(order*sizeof(int));
|
|
||||||
level = (signed char*)malloc(order*sizeof(int));
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
graph = graph_alloc(type);
|
|
||||||
prepare_graph(type, graph);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// finally do stuff
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
int counter = 0;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
while(fread(level, sizeof(signed char), order, infile) == order) {
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if((~left_invariant & left_invariant_wanted) == 0 && (~right_invariant & right_invariant_wanted) == 0) {
|
|
||||||
ngens = 0;
|
|
||||||
memset(generators, 0, order*sizeof(int));
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < order; j++) {
|
|
||||||
if(level[j] == HEAD_MARKER && generators[j] == 0) { // ignore the generator, if it is equivalent to one already seen
|
|
||||||
ngens++;
|
|
||||||
queue_init(&queue);
|
|
||||||
queue_put(&queue, j);
|
|
||||||
while((current = queue_get(&queue)) != -1) {
|
|
||||||
if(generators[current] == 0) { // visit everyone only once
|
|
||||||
generators[current] = ngens;
|
|
||||||
for(int k = 0; k < rank; k++) {
|
|
||||||
if(left_invariant & (1 << k))
|
|
||||||
queue_put(&queue, graph[current].left[k]);
|
|
||||||
if(right_invariant & (1 << k))
|
|
||||||
queue_put(&queue, graph[current].right[k]);
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
printf("left: ");
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < rank; j++)
|
|
||||||
printf("%c", left_invariant & (1 << j) ? alphabet[j] : ' ');
|
|
||||||
printf(" right: ");
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < rank; j++)
|
|
||||||
printf("%c", right_invariant & (1 << j) ? alphabet[j] : ' ');
|
|
||||||
printf(" generators: ");
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
memset(seen, 0, order*sizeof(int));
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < order; i++) {
|
|
||||||
if(generators[i] != 0 && seen[generators[i]-1] == 0) {
|
|
||||||
seen[generators[i]-1] = 1;
|
|
||||||
// if(type.n == 1 && type.factors[0].series == 'A')
|
|
||||||
// printf("%s ", stringify_SLn1_permutation(graph[i].word, graph[i].wordlength, rank, string_buffer1));
|
|
||||||
// else if(type.n == 1 && (type.factors[0].series == 'B' || type.factors[0].series == 'C'))
|
|
||||||
// printf("%s ", stringify_Onn1_permutation(graph[i].word, graph[i].wordlength, rank, string_buffer1));
|
|
||||||
// else
|
|
||||||
if(i == 0)
|
|
||||||
printf("1 ");
|
|
||||||
else
|
|
||||||
printf("%s ", alphabetize(graph[i].word, graph[i].wordlength, alphabet, string_buffer1));
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
printf("\n");
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if(infile != stdin)
|
|
||||||
fclose(infile);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// cleanup
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
graph_free(type, graph);
|
|
||||||
free(seen);
|
|
||||||
free(generators);
|
|
||||||
free(type.factors);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return 0;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
*/
|
|
||||||
41
old/test.c
41
old/test.c
@@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#include "weyl.h"
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
static void print_element(weylgroup_element_t *e)
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
if(e->wordlength == 0)
|
|
||||||
printf("1");
|
|
||||||
else
|
|
||||||
for(int j = 0; j < e->wordlength; j++)
|
|
||||||
printf("%c", e->word[j] + 'a');
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
int main()
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
semisimple_type_t type;
|
|
||||||
simple_type_t t;
|
|
||||||
type.n = 1;
|
|
||||||
type.factors = &t;
|
|
||||||
t.series = 'A';
|
|
||||||
t.rank = 3;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
int order = weyl_order(type);
|
|
||||||
doublequotient_t *dq = weyl_generate_bruhat(type, 0x02, 0x03);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < dq->count; i++) {
|
|
||||||
print_element(dq->cosets[i].min);
|
|
||||||
printf(" -> ");
|
|
||||||
for(doublecoset_list_t *current = dq->cosets[i].bruhat_lower; current; current = current->next) {
|
|
||||||
print_element(current->to->min);
|
|
||||||
printf(" ");
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
printf("| ");
|
|
||||||
print_element(dq->cosets[i].opposite->min);
|
|
||||||
printf("\n");
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
weyl_destroy_bruhat(dq);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return 0;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
@@ -110,7 +110,7 @@ static void generate_principal_ideals(doublequotient_t *dq, bitvec_t *pos, bitve
|
|||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#ifdef _DEBUG
|
#ifdef _DEBUG
|
||||||
if(is_slim[i]) {
|
if(is_slim[i] && dq->cosets[0].min) { // sometimes we don't want to define min and max
|
||||||
fprintf(stderr, " ids: [0");
|
fprintf(stderr, " ids: [0");
|
||||||
for(int j = 1; j < size; j++)
|
for(int j = 1; j < size; j++)
|
||||||
if(principal[j])
|
if(principal[j])
|
||||||
@@ -160,7 +160,7 @@ long enumerate_balanced_thickenings(doublequotient_t *dq, enumeration_callback c
|
|||||||
// the algorithm only works if the opposition pairing does not stabilize any element
|
// the algorithm only works if the opposition pairing does not stabilize any element
|
||||||
// if this happens, there can be no balanced thickenings
|
// if this happens, there can be no balanced thickenings
|
||||||
for(int i = 0; i < dq->count; i++)
|
for(int i = 0; i < dq->count; i++)
|
||||||
if(dq->cosets[i].opposite->min->id == dq->cosets[i].min->id)
|
if(dq->cosets[i].opposite->index == i)
|
||||||
return 0;
|
return 0;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// we can only handle bitvectors up to BV_BLOCKSIZE*BV_RANK bits, but we only store half of the weyl group
|
// we can only handle bitvectors up to BV_BLOCKSIZE*BV_RANK bits, but we only store half of the weyl group
|
||||||
|
|||||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user